Healing open wounds caused by skin picking
Online test
Find out the severity of your symptoms with this free online test
How your skin works
An adult's skin can weigh up to 3,6 kilograms and cover a space of about 2 metres.That makes your skin your body's largest and most important organ, providing you with an important defence against bacteria, diseases and germs that would threaten your health and well being. Your skin, which is made up of several different layers, is a waterproof agent that protects the nevers, bones, muscles and tendons within your body, keeping them in place; shields you against extremes such as harsh sunlight; harmful chemicals and it has healing properties within it that allows it to heal when injured. Your skin is made out of three main layers. The outmost layer of skin, called the epidermis is the layer that forms a waterproof barrier and gives you your skin tone. The second layer, the dermis, is the part that contains connective tissue, hair follicles and sweat glands whereas the third layer, the subcutaneous layer or hypodermis is the part made out of fat and connective tissue. When the skin is injured, cells within your body swiftly swings into action to ensure that the injured part is healed quickly.
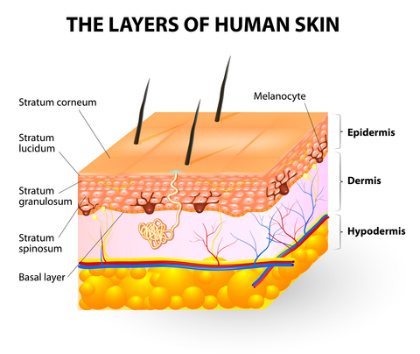
Image: skin-remedies.com
How your skin heals itself
The skin is an amazing organ in that when cared for properly, healing can occur quickly. The healing process can take as little as a few days to a few weeks, or in serious cases, longer. What is really interesting about your skin's healing abilities is how quickly your skin can regenerate, when cared for properly. Research shows that every day, your body is getting rid of up to 40,000 skin cells, which means the skin you see today will be different in a month's time. 
When a wound is inflicted on the skin, the body sends a message to the area and blood flow to the wounded area is restricted, enabling blood to clot around the wound, forming a scab. White blood cells fights off any form of possible infection and germs at the wound site and fibroblast, which are cells that can form new skin and tissue at the wound, produce collagen at the sit of the wound, creating new skin tissue. The scab will eventually fall off, leaving a scar, which will gradually fade away as time passes on.
It is important to bear in mind that not all wounds on the skin are equal, as wounds have four different stages. The first stage is that of red, blotchy, discoloured, inflamed skin characterised by swelling or hardness. The second stage is when the wound partially penetrates the skin, and the third state consists of thick wounds that do not penetrate through the white membrane that separates the skin and fat from deeper tissues. The fourth stage is when there has been damage inflicted on the muscle or bone and tissue in the area, including damage to blood vessels. The type of wound on your skin will determine the speed of the healing process and type of care or medical intervention needed to return the skin to a normal state.
Why skin picking is harmful to your skin
Compulsive Skin picking, also known as dermatillomania or excoriation disorder, while it may initially appear to be a harmless activity, can inflict damage on the skin in the long term, causing unsightly blotches and scars that can make people embarrassed to have their arms and legs exposed in public. As a result of this, people who pick at their skin either wear long sleeves and pants in public, or refuse to leave their homes due to concerns over their appearance.
Continuous picking at the skin, including scabs results in thicker scars and wounds that do not have enough time to heal properly. It must be remembered that the smaller the wound, the quicker it takes to heal and open wounds, which take longer to heal leave bigger scars. It is also important to bear in mind that if a wound takes longer to heal than normal, it may be an indication of an underlying health problem such as diabetes. Skin pickers pick at the skin and repick a wound because it may give them a sensation of relief in stressful, emotionally charged times. However, as the wound bleeds and is not given a chance to heal, the skin is more prone to infections and requires a longer period of time to heal properly. At times, the continuous action of skin picking can result in serious life threatening infections that compromise your immune system and result in hospitalisation, surgery and skin grafts where needed. Skin pickers have been known to break though to muscle and bone tissue, or even damage a major artery which require emergency attention.
Natural remedies and medical treatments for healing your skin
While there are different forms of therapies aimed at helping people to stop picking at their skin, there are a number of natural and medical remedies that may encourage you to stop picking at your skin. Medical treatments aimed at helping people to stop picking at their skin and promote skin healing are also used to help people with other types of obessesive compulsive disorders. Since dermatillomania is viewed as a mental illness or a psychological imbalance, medications like Selective Serotin Ruptake Inhibitors, doxepin, clomipramine, naltrexone, pimozide and olanzapine among others are oxepin, clomipramine, naltrexone, pimozide, and olanzapine are prescribed. It is important to bear in mind that not everyone responds in the same way to these medications. On the other hand, natural remedies which use natural ingredients found in our food or environment are a natural way of healing the skin.
Some of these natural remedies include using honey, which is known to be packed with antioxidants, amnio acids, vitamins and minerals to heal cuts and open wounds on the skin. Honey has been known to kill bacteria and fungi that infect wounds, and even in some cases, eliminate scars. When caring for your skin, it is important to keep it moist, and not let it dry out and crack. Moist skin also speeds up the healing process. Wearing gloves on your hands can play a role in helping you to fight the urge to pick at your skin.
Tea tree oil also has healing properties and is known to heal cuts and reduce inflammation. Lavender oil is known to keep infections at bay and relieve pain, whereas chamomile has been known to treat burns, bruises, cuts, scrapes, and even eczema. It is all about finding out what works for you best as one treatment that works for someone may not necessarily work for you.
Online test
Find out the severity of your symptoms with this free online test
Start your journey with SkinPick
Take control of your life and find freedom from skin picking through professional therapy and evidence-based behavioral techniques.
Start Now